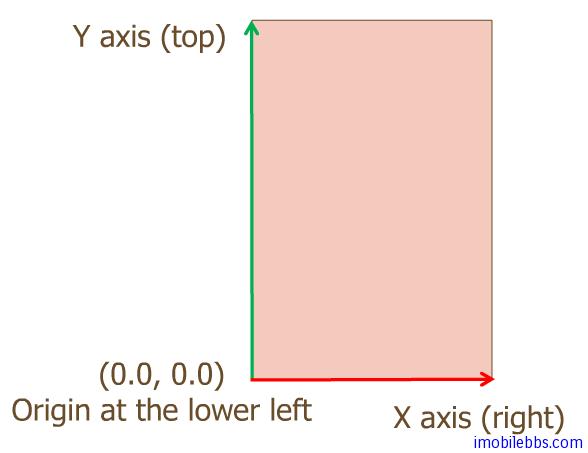
摄影师调整好相机和被拍摄物体的位置角度(modelview) ,对好焦距(projection)后,就可以按下快门拍照了,拍好的照片可以在计算机上使用照片浏览器查看照片,放大,缩小,拉伸,并可以将照片显示窗口在屏幕上任意拖放。对应到3D绘制就是Viewport 变换,目前的显示器大多还是2D的,viewport(显示区域)为一个长方形区域,并且使用屏幕坐标系来定义:
 OpenGL ES 中使用glViewport() 来定义显示视窗的大小和位置:
OpenGL ES 中使用glViewport() 来定义显示视窗的大小和位置:
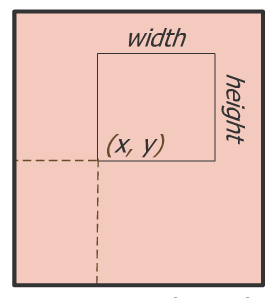
glViewport(int x, int y, int width, int height)
 Android 缺省将viewport 设置成和显示屏幕大小一致。
Android 缺省将viewport 设置成和显示屏幕大小一致。
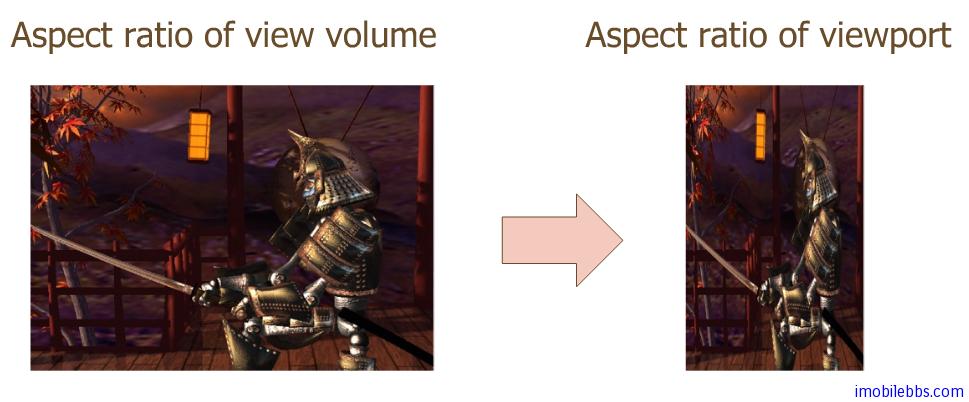
如果投影变换的宽度/高度比 (aspect) 和最后的Viewport 的width/height 比不一致的话,最后显示的图形就可能需要拉伸以适应Viewport,从而可能造成图像变形。比如:现在的电视的显示模式有4:3 和 16:9 或是其它模式,如果使用16:9的模式来显示原始宽高比为4:3的视频,图像就有变形。、
 Z 坐标变换
Z 坐标变换
前面提到的modelview, projection 变换 同样应用于Z轴坐标,但和屏幕坐标系中x,y 坐标不同的时,在屏幕坐标系下 ,Android OpenGL ES 将z 坐标重新编码,它的值总会在0.0到1.0之间。作为深度depth 测试的依据。
我们在示例代码的OpenGLRenderer的onSurfaceChanged 使用和屏幕一样大小的区域作为Viewport,你也可以通过glViewport将视窗设成屏幕的局部某个区域。
并且可以看到透视投影的aspect 为width/height ,因此最后的图形不会有变形:
public void onSurfaceChanged(GL10 gl, int width, int height) {
// Sets the current view port to the new size.
gl.glViewport(0, 0, width, height);
// Select the projection matrix
gl.glMatrixMode(GL10.GL_PROJECTION);
// Reset the projection matrix
gl.glLoadIdentity();
// Calculate the aspect ratio of the window
GLU.gluPerspective(gl, 45.0f,
(float) width / (float) height,
0.1f, 100.0f);
// Select the modelview matrix
gl.glMatrixMode(GL10.GL_MODELVIEW);
// Reset the modelview matrix
gl.glLoadIdentity();
}